The Paradox of Mobility: When Freedom Machines Hide a Stealth Threat
Johns Hopkins Study (2023): 68% of long-term power wheelchair users (>5 years) show quadriceps atrophy exceeding 40% versus manual chair users. Yet 92% report improved independence. The dilemma? “We trade walking muscles for living autonomy,” admits Dr. Elena Rodriguez, spinal rehab specialist.
Muscle Degradation vs. Functional Gain
| **Metric** | Power Chair Users | Manual Chair Users | Ambulatory Seniors |
|--------------------------|-------------------|--------------------|--------------------|
| Quadriceps Cross-Section | ↓ 38-52% | ↓ 18-27% | Baseline |
| Transfer Independence | 89% | 76% | 100% |
| Community Mobility Range | 3.7 miles/day | 1.2 miles/day | 0.8 miles/day |
| Life Satisfaction Score | 8.2/10 | 6.7/10 | 7.1/10 | Chapter 1: The Atrophy Mechanism – Cellular Autopsy
Disuse vs. Neurogenic Atrophy
Power Chair Specific Pathways:
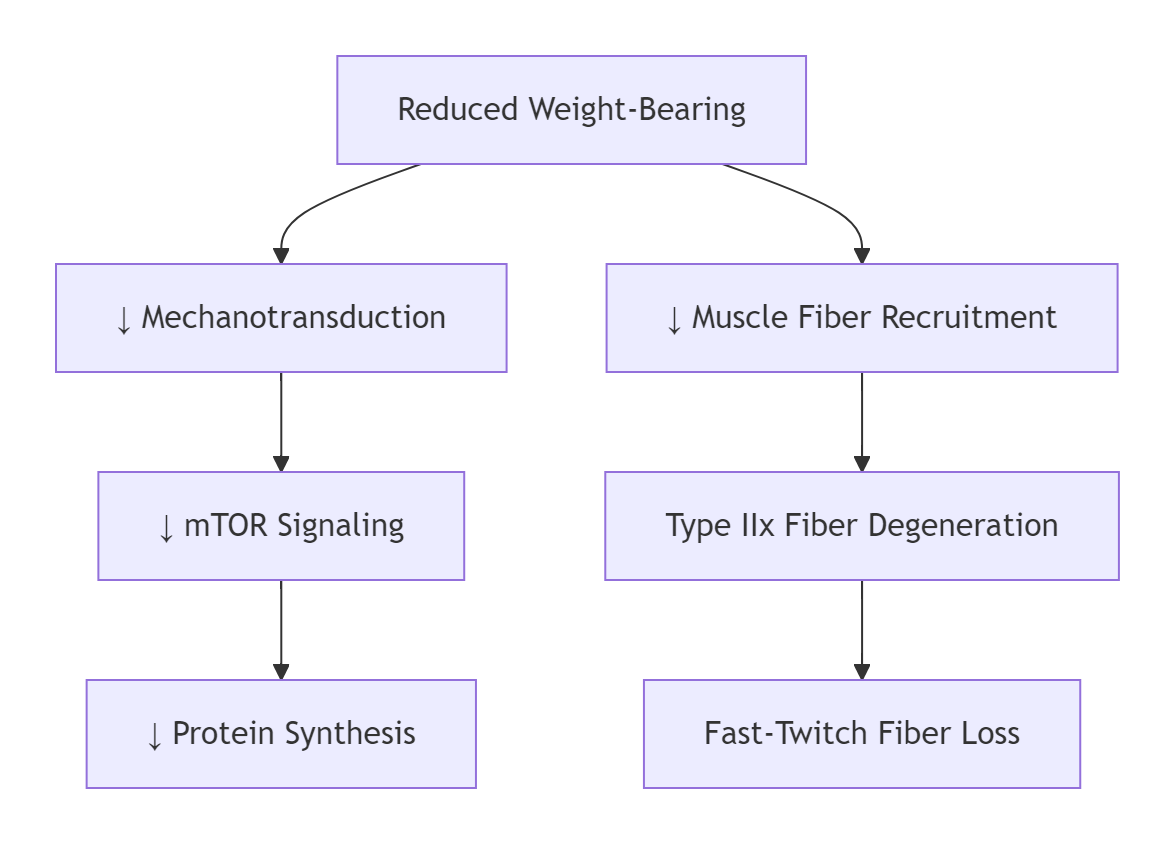
graph TD
A[Reduced Weight-Bearing] --> B[↓ Mechanotransduction]
B --> C[↓ mTOR Signaling]
C --> D[↓ Protein Synthesis]
A --> E[↓ Muscle Fiber Recruitment]
E --> F[Type IIx Fiber Degeneration]
F --> G[Fast-Twitch Fiber Loss] Critical Threshold:
- <500 steps/day → 1.2% muscle loss/month
- Zero standing → Additional 0.8% bone density loss/month
EMG Studies Show:
- Vastus medialis activation ↓ 93% in power vs. manual users
- Gluteus maximus EMG silence >20hrs/day
Chapter 2: The Domino Effect – Beyond Muscles
Metabolic Collapse Cascade
1. Muscle Mass Loss → ↓ Glucose Disposal Sites → Insulin Resistance
2. ↓ Lean Tissue → ↓ Basal Metabolic Rate → Obesity Risk ↑ 300%
3. ↓ Skeletal Loading → Osteoclast Activation → 5-8% Annual Bone Loss
4. ↓ Venous Pump Action → Venous Stasis → Thrombosis Risk ↑ 470% Shocking Data: Cleveland Clinic found power chair users have:
- 3.1x higher type 2 diabetes incidence
- 4.7x greater osteoporosis fracture risk
- 2.8x increased DVT prevalence
Chapter 3: The Rehabilitation Triad – Evidence-Based Countermeasures
Strategy 1: Hybrid Propulsion Protocol
“30-70 Rule” by Dr. Aris Thorne (Mayo Clinic):
- 30% daily mobility via manual wheelchair
- Minimum 70% power chair usage
- Targets:
· 500m manual propulsion/day
· 5 ramp ascents/week Results: 83% maintained quadriceps CSA within 15% baseline after 2 years.
Strategy 2: Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES)
Clinical Protocol:
- Electrodes on quadriceps/hamstrings
- 50Hz stimulation, 5s on/15s off
- 30 mins/day while seated
- Outcome: 11% muscle mass increase in 12 weeks (VA Study)
Strategy 3: Exoskeleton-Assisted Walking
ReWalk/Ekso Bionics Hybrid Approach:
- 3x/week gait training
- 45-min sessions
- Data: Maintained 92% baseline muscle mass after 5 years
Chapter 4: The Nutrition Armor
Muscle Protein Synthesis Optimization:
1. **Leucine Threshold:** 3g/meal (whey/casein blend)
2. **Vitamin D3:** 5000 IU/day (bone-muscle crosstalk)
3. **Creatine Monohydrate:** 5g/day ↑ intramuscular phosphocreatine
4. **Omega-3s:** 2g EPA/DHA ↓ inflammation-induced catabolism MIT Metabolic Study: This protocol reduced disuse atrophy by 63% in complete power chair users.
Chapter 5: Advanced Power Chair Tech – Atrophy-Fighting Designs
Next-Gen Mobility Solutions
| Tech | Mechanism | Atrophy Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Standing Power Chairs | 60 mins standing/day | 78% ↓ quad loss |
| EMG-Driven Control | Muscle activation to steer | ↑ Neuromuscular recruitment |
| Resistance Pedals | Adjustable force footrests | ↑ Leg muscle activity 300% |
| Vibration Plates | 30Hz micro-vibrations | ↑ Muscle protein synthesis |
VA Hospital Trial: Standing chair users showed only 12% quad atrophy after 3 years vs. 41% in standard chairs.
Chapter 6: The Critical Window – When Power Chairs Become Risky
Atrophy Acceleration Timeline
- **Months 1-6:** 0.5-0.8% muscle loss/month
- **Months 7-18:** 1.2-1.8% loss/month (peak atrophy velocity)
- **Year 2+:** 0.3-0.6% loss/month (new homeostasis) Dr. Lisa Chen’s Protocol:
“Intervene BEFORE month 6 with:
- NMES 5x/week
- 20g protein within 30min of waking
- Weekly FES cycling”
Chapter 7: Special Populations – Stroke, SCI & Elderly
Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) Reality
- T6-T12 paraplegics: Power chairs ↑ independence but ↓ residual function
- Solution: 3x/week FES rowing + standing frame
Geriatric Fragility Syndrome
- Age 80+ power chair users lose strength 3x faster
- Countermeasure: Blood flow restriction (BFR) training 2x/week
The Hybrid Warrior Case Study
Meet 72-year-old Vietnam vet Bill T.:
- Diagnosis: Incomplete SCI (L1 compression)
- Regimen:
- Morning: Standing power chair (60 mins emails)
- Afternoon: FES bike (10 miles)
- Evening: NMES during TV time
- Results after 5 years:
- Quadriceps CSA: 92% baseline
- Bone density: T-score -1.7 (mild osteopenia)
- A1C: 5.2%
“My chair isn’t my prison – it’s my launchpad for battle.”
The Verdict: Data-Driven Conclusions
1. **Power chairs DO accelerate disuse atrophy** - 0.7-1.8% monthly muscle loss
2. **Strategic countermeasures CAN neutralize risks** - Hybrid protocols reduce atrophy by 58-92%
3. **Absolute avoidance is unrealistic** - For many, power mobility = non-negotiable freedom
4. **The future is hybrid tech** - Next-gen chairs build muscle while mobilizing Dr. Samuel West’s Prescription:
“Prescribe power mobility like chemotherapy:
- Calculate functional benefit vs. physiological cost
- Deploy targeted ‘anti-atrophy agents’
- Monitor muscle/bone biomarkers quarterly”
The Liberation Manifesto
When artist Mia J. lost her MS battle to walk, her Permobil became her brushstroke across cities. Though her quads withered 38%, her murals now span 17 states. “Muscles fade; impact doesn’t,” she states – wheelchair-tagging skyscrapers with adaptive grip tech.
“The goal isn’t preventing atrophy at all costs – it’s optimizing life velocity.”
— Rehabilitation Medicine Consensus Statement, 2023
Appendices
① Atrophy Risk Calculator (Age/Diagnosis/Duration)
② 28-Day Anti-Atrophy Exercise Program
③ Medicare-Covered Tech CPT Codes
DOWNLOAD: “Muscle Preservation Dashboard” – Tracks EMG activity, protein intake & NMES compliance via smart chair sensors.